Label transfer from scRNA-seq dataset via Pearson correlation#
In this notebook, we will show how to transfer labels from a reference single-cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq) dataset via a lightweight approach. We will use Pearson correlation to find the celltype with the highest expression correlation for each cell the spatial transcriptomics datasset, according to CellSPA.
Load scRNA-seq dataset#
We use the scRNA-seq dataset of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) samples from Dong et al. published on CellxGene.
[1]:
from pathlib import Path
import anndata as ad
scRNAseq_data_path = Path("/g/huber/projects/CODEX/segtraq/data/label_transfer/scRNA_seq_DLBCL_matched_with_2_C1.h5ad")
adata_ref = ad.read(scRNAseq_data_path)
/home/lazic/miniforge3/envs/sc_analysis_sdata/lib/python3.10/site-packages/anndata/__init__.py:42: FutureWarning: `anndata.read` is deprecated, use `anndata.read_h5ad` instead. `ad.read` will be removed in mid 2024.
warnings.warn(
[2]:
adata_ref
[2]:
AnnData object with n_obs × n_vars = 29184 × 442
obs: 'cell_type', 'is_primary_data', 'sample_id'
The counts in the reference dataset are already log-normalized, so we can copy that matrix to a layer called ‘logcounts’.
[3]:
adata_ref.X.toarray()
[3]:
array([[0. , 0. , 0. , ..., 0. , 0. ,
0. ],
[0. , 0. , 0. , ..., 0. , 0. ,
0. ],
[0. , 0. , 2.38975334, ..., 0. , 0. ,
0. ],
...,
[0. , 0. , 0. , ..., 0. , 0. ,
0. ],
[0. , 0. , 0. , ..., 0. , 0. ,
0. ],
[0. , 0. , 0. , ..., 0. , 0. ,
0. ]], shape=(29184, 442))
[4]:
adata_ref.layers["logcounts"] = adata_ref.X.copy()
We aggregate log-normalized gene expression values (logcounts) across cells grouped by their annotated cell type, computing the mean expression per gene within each cell type. This yields a reference expression profile for each cell type.
[5]:
import numpy as np
logcounts = adata_ref.layers["logcounts"]
# If it's sparse, convert to dense
if not isinstance(logcounts, np.ndarray):
logcounts = logcounts.toarray()
celltypes = adata_ref.obs["cell_type"]
[6]:
import pandas as pd
logcounts_df = pd.DataFrame(logcounts, columns=adata_ref.var_names)
logcounts_df["celltype"] = celltypes.values
ref_mean_df = logcounts_df.groupby("celltype").mean()
/tmp/ipykernel_3092810/2272690639.py:6: FutureWarning: The default of observed=False is deprecated and will be changed to True in a future version of pandas. Pass observed=False to retain current behavior or observed=True to adopt the future default and silence this warning.
ref_mean_df = logcounts_df.groupby("celltype").mean()
[7]:
ref_mean_df
[7]:
| A2M | ABCA1 | ACACA | ACADM | ACKR1 | ACKR4 | ACTA2 | ADAM10 | ADAM17 | ADCY7 | ... | IL9 | IGLC3 | HMGB1 | GNAS | IL22 | IGLC2 | DRAIC | ANGPT2 | ICOSLG | IL6ST | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| celltype | |||||||||||||||||||||
| B | 0.000000 | 0.016769 | 0.156024 | 0.159486 | 0.000000 | 0.022256 | 0.050791 | 0.213838 | 0.229673 | 0.270148 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| DC_pc | 0.036694 | 0.169812 | 0.117063 | 0.444065 | 0.004440 | 0.003707 | 0.140305 | 0.437622 | 0.294588 | 0.784672 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Endothelia | 1.471162 | 0.178528 | 0.270104 | 0.289596 | 0.885165 | 0.013624 | 0.112109 | 0.361705 | 0.256111 | 0.163421 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Epithelia | 0.019746 | 0.080427 | 0.254660 | 0.178775 | 0.001124 | 0.026345 | 0.017461 | 0.119152 | 0.206132 | 0.108029 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Fibro_Muscle | 0.266040 | 0.312430 | 0.264807 | 0.343359 | 0.072844 | 0.003145 | 0.434594 | 0.369848 | 0.277516 | 0.193193 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Mono_Macro | 0.656003 | 0.890168 | 0.149249 | 0.331428 | 0.014655 | 0.002430 | 0.114052 | 0.358778 | 0.334295 | 0.585345 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| NK | 0.021211 | 0.106054 | 0.201798 | 0.357114 | 0.005284 | 0.000000 | 0.101637 | 0.559331 | 0.245895 | 0.659352 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Pericyte | 2.253352 | 0.360183 | 0.252609 | 0.435539 | 0.326374 | 0.000000 | 0.803320 | 0.553716 | 0.318709 | 0.157481 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| T_CD4 | 0.029272 | 0.077661 | 0.152805 | 0.257307 | 0.008759 | 0.000000 | 0.137884 | 0.459278 | 0.233179 | 0.363228 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| T_CD8 | 0.031461 | 0.045086 | 0.151711 | 0.311616 | 0.004273 | 0.001105 | 0.106523 | 0.336085 | 0.214291 | 0.386563 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| T_dividing | 0.051053 | 0.032399 | 0.196901 | 0.487031 | 0.003520 | 0.000000 | 0.150578 | 0.765854 | 0.408252 | 0.345907 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Tumor_DLBCL | 0.017330 | 0.074456 | 0.278579 | 0.419433 | 0.004762 | 0.000889 | 0.196989 | 0.418151 | 0.366993 | 0.365700 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| cDC | 0.077264 | 0.341498 | 0.163797 | 0.296956 | 0.021874 | 0.005103 | 0.095915 | 0.394451 | 0.305254 | 0.900343 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
13 rows × 442 columns
Load spatialData object#
Next, we load the spatialdata object of a Xenium DLBCL sample.
[8]:
import spatialdata as sd
sdata = sd.read_zarr(
"/g/huber/projects/GSK_lazic/B_NHL/BNHL_RICOVER/tma_2/2_C1/proseg_output/spatialData_2_C1_proseg.zarr"
)
/home/lazic/miniforge3/envs/sc_analysis_sdata/lib/python3.10/site-packages/dask/dataframe/__init__.py:31: FutureWarning: The legacy Dask DataFrame implementation is deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Set the configuration option `dataframe.query-planning` to `True` or None to enable the new Dask Dataframe implementation and silence this warning.
warnings.warn(
/home/lazic/miniforge3/envs/sc_analysis_sdata/lib/python3.10/site-packages/xarray_schema/__init__.py:1: UserWarning: pkg_resources is deprecated as an API. See https://setuptools.pypa.io/en/latest/pkg_resources.html. The pkg_resources package is slated for removal as early as 2025-11-30. Refrain from using this package or pin to Setuptools<81.
from pkg_resources import DistributionNotFound, get_distribution
version mismatch: detected: RasterFormatV02, requested: FormatV04
/home/lazic/miniforge3/envs/sc_analysis_sdata/lib/python3.10/site-packages/zarr/creation.py:614: UserWarning: ignoring keyword argument 'read_only'
compressor, fill_value = _kwargs_compat(compressor, fill_value, kwargs)
We perform quality control steps (filtering based on #transcripts and #genes per cell) and log-normalization.
[9]:
adata = sdata["table"]
[131]:
import scanpy as sc
import segtraq as st
# Compute QC metrics
transcript_counts = st.bl.transcripts_per_cell(sdata)
gene_counts = st.bl.genes_per_cell(sdata)
transcript_counts.index = transcript_counts.index.astype(str)
gene_counts.index = gene_counts.index.astype(str)
transcript_counts_filtered = transcript_counts.loc[adata.obs_names]
gene_counts_filtered = gene_counts.loc[adata.obs_names]
adata.obs["total_transcripts"] = transcript_counts_filtered["transcript_count"]
adata.obs["total_genes"] = gene_counts_filtered["gene_count"]
[144]:
adata.obs
[144]:
| centroid_x | centroid_y | cell_size | axis_minor_length | axis_major_length | centroid-0 | centroid-1 | eccentricity | solidity | perimeter | sample_id | TMA | region | mask_id | total_transcripts | total_genes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cell_id | ||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 377.79850 | 513.17664 | 395.71875 | 6.590376 | 8.878127 | 512.720930 | 376.953488 | 0.670050 | 0.860000 | 24.899495 | 2_C1 | 2 | cell_labels | 1 | 993 | 73 |
| 2 | 349.86170 | 643.56384 | 92.53125 | 2.653300 | 5.366563 | 643.600000 | 349.000000 | 0.869227 | 0.500000 | 0.000000 | 2_C1 | 2 | cell_labels | 2 | 985 | 89 |
| 3 | 401.73760 | 398.32178 | 397.68750 | 5.502993 | 9.527791 | 396.305556 | 400.916667 | 0.816339 | 0.800000 | 21.071068 | 2_C1 | 2 | cell_labels | 3 | 959 | 136 |
| 4 | 257.44656 | 319.80533 | 773.71875 | 9.718573 | 11.625859 | 319.301205 | 257.168675 | 0.548814 | 0.813725 | 34.384776 | 2_C1 | 2 | cell_labels | 4 | 932 | 161 |
| 5 | 195.35858 | 549.35860 | 194.90625 | 3.843169 | 5.055352 | 548.785714 | 194.928571 | 0.649668 | 0.875000 | 11.414214 | 2_C1 | 2 | cell_labels | 5 | 926 | 47 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 5843 | 539.39000 | 343.35000 | 196.87500 | 6.445665 | 16.611864 | 343.063492 | 539.158730 | 0.921653 | 0.684783 | 40.798990 | 2_C1 | 2 | cell_labels | 5843 | 61 | 85 |
| 5844 | 256.99690 | 636.03420 | 316.96875 | 7.896618 | 12.941854 | 636.506667 | 256.333333 | 0.792277 | 0.842697 | 35.142136 | 2_C1 | 2 | cell_labels | 5844 | 61 | 41 |
| 5845 | 310.64035 | 493.85090 | 112.21875 | 6.976622 | 7.382183 | 493.272727 | 310.151515 | 0.326891 | 0.733333 | 24.727922 | 2_C1 | 2 | cell_labels | 5845 | 60 | 109 |
| 5846 | 366.64166 | 153.53334 | 236.25000 | 8.121170 | 12.488528 | 152.528571 | 366.328571 | 0.759686 | 0.777778 | 36.556349 | 2_C1 | 2 | cell_labels | 5846 | 60 | 46 |
| 5847 | 494.74417 | 190.87209 | 169.31250 | 8.103957 | 8.811781 | 190.180000 | 494.300000 | 0.392685 | 0.847458 | 26.384776 | 2_C1 | 2 | cell_labels | 5847 | 60 | 33 |
5845 rows × 16 columns
[133]:
# Filter outliers
qc_range = {"total_transcripts": (10, 2000), "total_genes": (5, np.inf)}
for key, (low, high) in qc_range.items():
mask = (adata.obs[key] >= low) & (adata.obs[key] <= high)
adata = adata[mask.to_numpy()].copy()
[134]:
# Normalize and log-transform
sc.pp.normalize_total(adata, target_sum=1e4)
sc.pp.log1p(adata)
adata.layers["logcounts"] = adata.X.copy()
/home/lazic/miniforge3/envs/sc_analysis_sdata/lib/python3.10/site-packages/legacy_api_wrap/__init__.py:82: UserWarning: Some cells have zero counts
return fn(*args_all, **kw)
Label transfer via correlation#
Now, we compute the Pearson correlation between each query cell in the processed AnnData object and the mean expression profiles of reference cell types.
We first identify the common genes between the query data and the reference matrix, and then compute a correlation matrix where each entry reflects the similarity between a query cell and a reference cell type.
For each query cell, we:
Assign the most correlated reference cell type (i.e., the one with the highest Pearson correlation),
Store both the correlation value and the predicted cell type.
This provides a label transfer from the reference to the query dataset based on global transcriptomic similarity.
[ ]:
from anndata import AnnData
from scipy.spatial.distance import cdist
def assign_celltype_by_pearson(adata: AnnData, ref_mean_df: pd.DataFrame, layer: str = "logcounts") -> pd.DataFrame:
"""
Assigns cell types to cells in `adata` by computing Pearson correlation
with reference expression profiles.
Parameters
----------
adata : AnnData
Query dataset with gene expression data in the specified layer.
ref_mean_df : pd.DataFrame
Reference expression matrix with shape (cell_types x genes).
layer : str, default="logcounts"
Layer in `adata` to use for expression values.
Returns
-------
pd.DataFrame
DataFrame with `cell_id` and assigned `celltype`.
"""
# TODO - check if cdist does really Pearson correlation
# Extract query expression data
X_query = pd.DataFrame(
(adata.layers[layer].toarray() if hasattr(adata.layers[layer], "toarray") else adata.layers[layer]),
index=adata.obs_names,
columns=adata.var_names,
)
# Align gene order
common_genes = X_query.columns.intersection(ref_mean_df.columns)
if len(common_genes) == 0:
raise ValueError("No common genes found between query and reference.")
X_query = X_query[common_genes]
X_ref = ref_mean_df[common_genes]
# Compute Pearson correlation (1 - correlation distance)
cor_mat = 1 - cdist(X_query.values, X_ref.values, metric="correlation")
cor_mat_df = pd.DataFrame(cor_mat, index=adata.obs_names, columns=X_ref.index)
# Assign best-matching reference cell type
best_celltype = cor_mat_df.idxmax(axis=1)
# Return as DataFrame
return pd.DataFrame({"cell_id": adata.obs_names, "celltype": best_celltype.values})
[146]:
result_df = assign_celltype_by_pearson(adata, ref_mean_df)
/tmp/ipykernel_2382657/4082630372.py:48: FutureWarning: The behavior of DataFrame.idxmax with all-NA values, or any-NA and skipna=False, is deprecated. In a future version this will raise ValueError
best_celltype = cor_mat_df.idxmax(axis=1)
[158]:
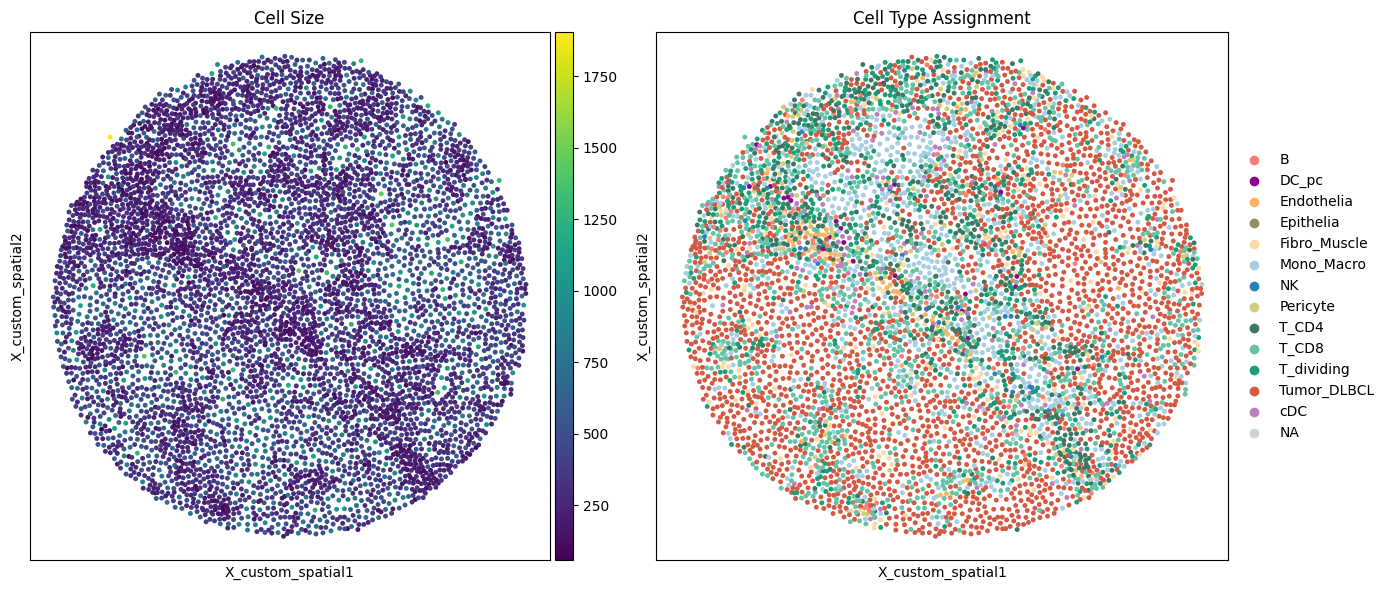
result_df["celltype"].value_counts()
[158]:
celltype
Tumor_DLBCL 2293
T_CD8 952
Mono_Macro 789
T_CD4 599
T_dividing 521
Fibro_Muscle 204
cDC 134
Pericyte 123
B 100
Endothelia 62
NK 35
DC_pc 23
Epithelia 6
Name: count, dtype: int64
[156]:
result_df.set_index("cell_id", inplace=True)
adata.obs["celltype_corr"] = result_df.loc[adata.obs_names, "celltype"]
[163]:
# define colors for cell types
col_celltype = {
"B": "#fb8072",
"cDC": "#bc80bd",
"DC_pc": "#910290",
"Endothelia": "#fdb462",
"Epithelia": "#959059",
"Fibro_Muscle": "#fed9a6",
"Mono_Macro": "#a6cee3",
"NK": "#2782bb",
"Pericyte": "#d2cd7e",
"T_CD4": "#3c7761",
"T_CD4_reg": "#66a61e",
"T_CD8": "#66c2a5",
"T_dividing": "#1b9e77",
"Tumor_DLBCL": "#d45943",
}
[170]:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Set up side-by-side plots
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(14, 6))
# Plot 1: Cell size
sc.pl.embedding(
adata,
basis="X_custom_spatial",
color="cell_size",
size=50,
ax=axs[0],
show=False,
title="Cell Size",
)
# Plot 2: Cell types with custom colors
sc.pl.embedding(
adata,
basis="X_custom_spatial",
color="celltype_corr",
size=50,
palette=col_celltype, # your custom palette from before
ax=axs[1],
show=False,
title="Cell Type Assignment",
)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()